Mishra in friction stir processing for enhanced low temperature formability 2014.
In sheet metal operations the volume of material reduced significantly.
It is customary to refer to a material below the thickness of 6 35 mm as a sheet and thicker materials as plate.
14 4 which of the following is typical of the starting work geometry in sheet metal processes.
The choice of materials depends on the requirements of the application and factors in material selection include formability weldability corrosion resistance strength weight and cost.
Even though a formed part has more surface area which is why the solid model adds the volume to the part it actually has the same volume because of material.
This distance is equal to the material thickness.
Sheet metal is metal formed by an industrial process into thin flat pieces.
Because this book is limited to bend forming which is the.
This doesn t reflect what really happens at the punch press.
The applied force stresses the metal beyond its yield strength causing the material to plastically deform but not to fail.
Thicknesses can vary significantly.
Sheet metal is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking and it can be cut and bent into a variety of shapes countless everyday objects are fabricated from sheet metal.
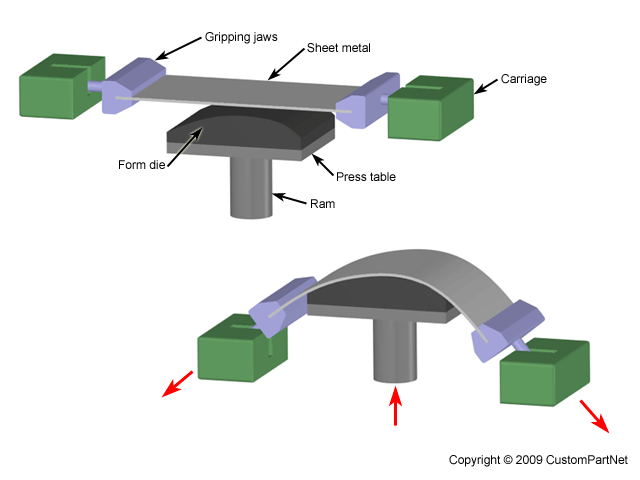
Forming and related operations performed on metal sheets strips and coils high surface area to volume ratio of starting metal which distinguishes these from bulk deformation often called pressworking because presses perform these operations parts are called stampings usual tooling.
Extremely thin sheets are considered foil or leaf and pieces thicker than 6 mm 0 25 in are considered.
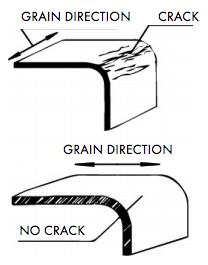
By doing so the sheet can be bent or stretched into a variety of complex shapes.
Sheet metal forming is quite common for making shaped components from soda cans to automotive car bodies.
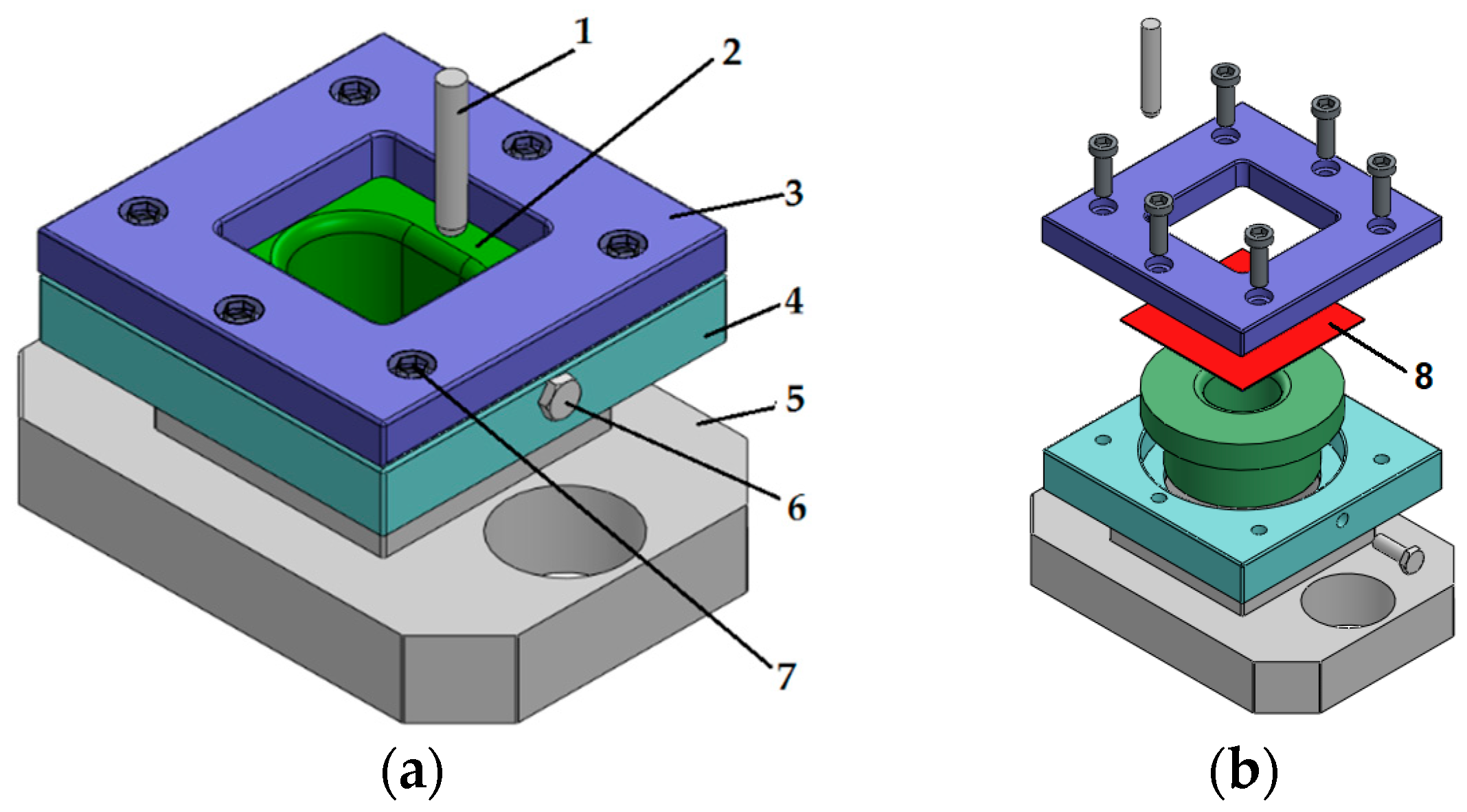
The main feature of any sheet metal part is a flange which consists of two parallel planar faces located in front of each other with some solid volume between them on the distance which is significantly smaller than the linear size of the faces.
Sheet metal forming processes are those in which force is applied to a piece of sheet metal to modify its geometry rather than remove any material.
Varied metals and metal alloys can be formed into sheets and used to fabricate sheet metal parts.
A elastic region or b plastic region.
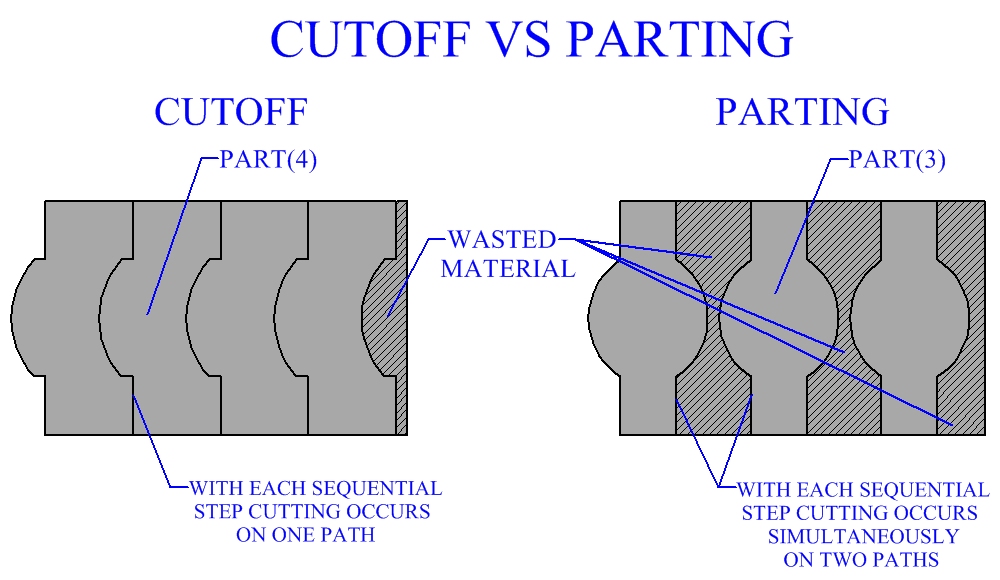
Most of the sheet metal cutting processes discussed can be performed on both sheet and plate metal although for many sheet metal operations difficulties will arise with increasing plate thickness.
If the reduction is large enough draw stress will exceed the yield strength of the exiting metal.
Popular sheet metal materials include.
When that happens the drawn wire will simply elongate instead of new material being squeezed through the die opening.
A high volume to area ratio or b low volume to area ratio.
The difference is that sheet metal is under 1 4 inch 6mm in thickness while plate metal is thicker.